The Complete Guide to Screen Printing Supplies: Machines, Inks, Accessories, and More
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about screen printing supplies, including types of screen printing machines, screens, specialty inks, drying equipment, and essential accessories. Whether you are a beginner lookScreen printing has become a go-to method for creating custom apparel, accessories, posters, and many other products. Its versatility, affordability, and ability to produce vibrant, durable designs make it popular across industries. From custom t-shirts and tote bags to posters and signage, screen printing offers endless possibilities for creativity and business opportunities.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about screen printing supplies, including types of screen printing machines, screens, specialty inks, drying equipment, and essential accessories. Whether you are a beginner looking to get started or an experienced printer looking to upgrade your setup, this guide will help you make informed decisions and improve your printing process.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Screen Printing
- Types of Screen Printing Machines and Presses
- Screen Types and Mesh Considerations
- Inks for Screen Printing
- Squeegees: Choosing the Right One
- Screen Coating and Exposure Units
- Chemicals and Cleaners for Screen Maintenance
- Heat Transfer and Curing Equipment
- Printing Accessories and Tools
- Blank Apparel and Textiles for Screen Printing
- Design Tools and Software for Screen Printing
- Specialized Screen Printing Tools and Supplies
- Advanced Techniques and Customization Options
- Common Challenges and Solutions in Screen Printing
- Conclusion: Building Your Screen Printing Business
1. Introduction to Screen Printing
Screen printing, also known as silk screen printing, is a printing technique that has been around for centuries. It involves creating a stencil (the screen) and using it to apply layers of ink on the printing surface. Each color requires a separate screen, and the process is repeated until the design is complete. This technique is renowned for its vibrant, bold prints and is widely used for products like t-shirts, posters, bags, signage, and more.

The History of Screen Printing
Screen printing originated in China during the Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD), where it was used for decorating fabrics. The technique gradually spread across Asia and was introduced to Europe in the 18th century. By the 20th century, screen printing had become widely popular in the commercial world, particularly for advertising and textile production. With advancements in technology and the development of new materials, screen printing has evolved into a highly efficient and versatile printing method that remains essential in today’s world of mass production and customization.
Why Screen Printing Is So Popular
There are several reasons why screen printing remains a popular method:
- Versatility: Screen printing can be used on a variety of materials, including fabrics, paper, wood, glass, and metal. This makes it suitable for a wide range of products, from apparel to packaging and promotional items.
- Durability: Screen-printed designs are long-lasting and resistant to wear and tear, making them ideal for items that require frequent use, such as t-shirts, tote bags, and outdoor signage.
- Cost-effectiveness: Once the initial setup is complete, screen printing becomes highly cost-effective for bulk production. The cost per item decreases significantly as the production volume increases, making it ideal for large orders.
- Quality: Screen printing produces bold, vibrant colors that are difficult to achieve with other printing methods. The ability to layer inks allows for more detailed and durable designs, resulting in high-quality prints that stand out.
Applications of Screen Printing
Screen printing is used in various industries for different applications:
- Apparel: Custom t-shirts, hoodies, and hats are some of the most common products printed using screen printing. The ability to print in bulk makes it a favorite for promotional clothing, events, and branding.
- Posters and Signs: Screen printing is often used for creating posters, banners, and signs due to its ability to produce sharp, vibrant images that capture attention.
- Promotional Products: Businesses use screen printing for promotional items like tote bags, mugs, and pens. The technique allows for mass production of branded merchandise at a relatively low cost.
- Textiles and Home Goods: Pillowcases, tablecloths, curtains, and other home textiles are often screen-printed to add decorative patterns and designs.
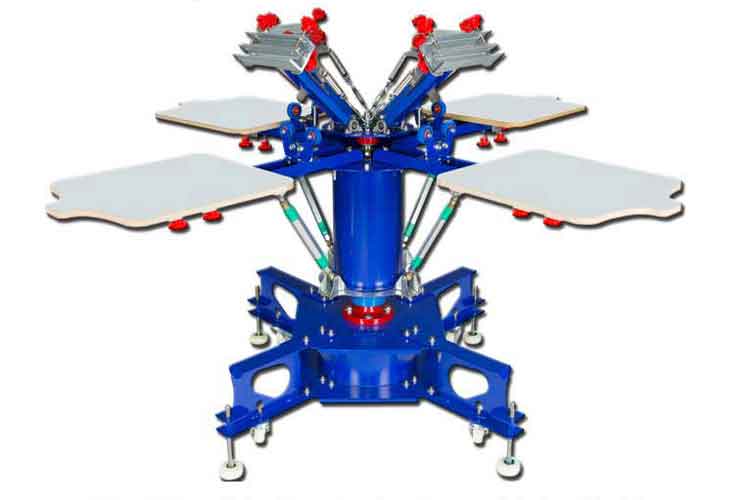
2. Types of Screen Printing Machines and Presses
Choosing the right screen printing machine is crucial to the success of your screen printing business. Different machines offer different levels of automation, production capacity, and versatility. Depending on your budget, production needs, and space, you’ll need to carefully evaluate which press is best suited to your operation.
Manual Screen Printing Presses
Manual screen printing presses are operated by hand and are perfect for small-scale operations or those just starting in the screen printing business. These presses allow you to control each aspect of the printing process, from the amount of ink applied to the pressure exerted on the screen. They’re ideal for small production runs, custom designs, and learning the craft.
- 1-Color Press: A simple press designed to print a single color at a time. This is suitable for very basic designs or for hobbyists looking to print small batches. It's affordable and compact, making it perfect for limited space.
- 4-Color Press: This type of press allows you to print multi-color designs by manually aligning the screens for each color. It’s a popular choice for small businesses, as it offers a balance between functionality and cost.
- 6-Color Press: Designed for more complex, multi-color prints. It’s ideal for businesses that want to print detailed designs or those looking to expand their production capacity.
Advantages of Manual Presses
- Cost-effective: Manual presses are significantly cheaper than automatic machines, making them accessible for startups or small businesses.
- Flexibility: You can print small runs of custom designs without the need for extensive setup, making manual presses ideal for personalized or low-volume orders.
- Control: Manual presses give the printer complete control over the process, allowing for adjustments in pressure, ink application, and registration.
Challenges of Manual Presses
- Time-consuming: Manual presses require more time and effort compared to automatic presses, especially for multi-color designs where each screen must be aligned manually.
- Labor-intensive: Manual screen printing can be physically demanding, particularly for larger orders, as each print requires the printer to apply pressure to the screen.
Automatic Screen Printing Machines
Automatic screen printing machines are designed for high-volume production. They use mechanical systems to automate the printing process, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing efficiency. These machines are perfect for businesses that need to print large orders quickly and consistently.
- Automatic Multi-color Presses: These machines are capable of printing multiple colors in one go, making them ideal for complex designs. The automation ensures precise alignment of each color, resulting in high-quality prints with minimal human error.
- All-in-One Automatic Machines: Some machines combine screen exposure, printing, and drying into a single system, streamlining the production process. These machines are designed for maximum efficiency and are commonly used in large-scale manufacturing.
Advantages of Automatic Presses
- Efficiency: Automatic presses can print thousands of items in a fraction of the time it would take with a manual press. This is particularly useful for businesses handling large orders or those with tight deadlines.
- Consistency: Automation ensures that each print is identical, minimizing the risk of human error and ensuring high-quality, consistent results.
- Labor-saving: Automatic presses reduce the need for manual labor, allowing businesses to increase production without adding additional staff.
Challenges of Automatic Presses
- High Cost: Automatic presses are a significant investment, making them less accessible to small businesses or startups. The initial cost can be high, but the return on investment is worthwhile for high-volume operations.
- Space Requirements: Automatic machines are larger and require more space, making them less suitable for small workshops or home-based businesses.
- Maintenance: Automated systems require regular maintenance to keep them functioning optimally, which can add to the operational costs.
Tabletop Presses
For those with limited space or budget, tabletop presses are an excellent option. These compact presses are easy to set up, portable, and offer a cost-effective solution for small-scale or hobbyist screen printers. They are often used for printing small quantities of products like t-shirts, tote bags, and posters.
Advantages of Tabletop Presses
- Portability: Tabletop presses are small and lightweight, making them easy to move and store.
- Affordable: They are much cheaper than larger manual or automatic presses, making them a great option for beginners or those with limited budgets.
- Versatility: Tabletop presses can be used for a variety of printing projects, from apparel to paper goods.
Challenges of Tabletop Presses
- Limited Capacity: Tabletop presses are not suitable for large production runs due to their size and manual operation.
- Less Precision: These presses may not offer the same level of precision as larger manual or automatic presses, which can affect the quality of the final product.
3. Screen Types and Mesh Considerations
The screen is the heart of the screen printing process. Choosing the right type of screen and mesh count is crucial to achieving the best results for your specific project. Different mesh counts, materials, and frames can significantly impact the final product, and understanding these differences will help you make the best choices for your printing needs.
Pre-stretched Screens
Pre-stretched screens are the most common type of screens used in screen printing. These screens come ready to use, with the mesh already stretched across the frame. They are available in various sizes and mesh counts, making them suitable for a wide range of projects.
- Aluminum Frames: Aluminum frames are lightweight, durable, and resistant to warping. They’re a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals due to their longevity and ease of handling.
- Wooden Frames: Wooden frames are cheaper but less durable. Over time, wooden frames can warp or absorb moisture, affecting the tension of the mesh. They are best suited for short-term use or one-time projects.
Rolls of Mesh
For screen printers who prefer to stretch their own screens, rolls of mesh are available in various materials and mesh counts. This option allows for greater customization and control over the tension and size of the screens.
- Polyester Mesh: Polyester is the most commonly used material for screen printing mesh. It offers excellent durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for most printing applications.
- Stainless Steel Mesh: Stainless steel mesh is stronger and more durable than polyester, making it suitable for high-volume printing or applications that require extreme precision. However, it is more expensive and less flexible.
Choosing the Right Mesh Count
Mesh count refers to the number of threads per inch in the screen mesh. The higher the mesh count, the finer the mesh, and the more detailed the print. The right mesh count depends on the type of ink, the level of detail in the design, and the material being printed.
- Low Mesh Count (60–110): Ideal for printing on coarse or textured surfaces, such as canvas or wood. Low mesh counts are also used for printing large, bold designs with thick layers of ink.
- Medium Mesh Count (155–230): Suitable for most apparel printing, especially t-shirts. This mesh count provides a good balance between ink flow and detail, making it a versatile choice for many projects.
- High Mesh Count (305+): Best for printing highly detailed designs, such as fine line work or halftones. High mesh counts are also used for printing on smooth surfaces, like paper or plastic, where minimal ink is required.
How Mesh Count Affects Ink Deposits
The mesh count of your screen affects the amount of ink deposited on the surface. Lower mesh counts allow more ink to pass through, resulting in thicker prints with a raised texture. Higher mesh counts deposit less ink, resulting in a smoother, more detailed print. Choosing the right mesh count is essential for achieving the desired look and feel of your final product.
Proper Screen Tension
Screen tension refers to how tightly the mesh is stretched across the frame. Proper screen tension is crucial for achieving sharp, clean prints. If the screen is too loose, the mesh can sag, causing blurry or uneven prints. If the screen is too tight, it may cause the mesh to tear or warp.
To maintain proper screen tension, it’s essential to regularly check and adjust your screens. Over time, screens can lose tension due to wear and tear, and they may need to be re-stretched or replaced.
4. Inks for Screen Printing
Inks are a critical component of the screen printing process. The right ink can determine the quality, durability, and overall appearance of the final product. Various types of inks are available, each with its own characteristics and suitable applications. Understanding the differences between them will help you choose the right ink for your screen printing projects.
Plastisol Ink
Plastisol ink is one of the most commonly used inks in screen printing, particularly for printing on textiles such as t-shirts, hoodies, and other apparel. It’s a durable, versatile ink that remains wet until it is cured with heat, allowing the printer to take time in perfecting the print before finalizing it.
-
Pros:
- Durability: Plastisol ink creates long-lasting prints that can withstand multiple washes without fading or cracking.
- Vibrant Colors: This ink produces bold, opaque colors that stand out, even on dark fabrics.
- Extended Working Time: Since plastisol ink doesn’t dry until it is cured, you can leave the screen loaded with ink without worrying about it drying out during the printing process.
-
Cons:
- Heat Curing Required: Plastisol ink needs to be cured at high temperatures (around 320°F or 160°C) for it to set properly. This requires the use of a flash dryer or conveyor dryer, which adds to the cost of equipment.
- Feel: Plastisol ink tends to create a thicker print with a slightly raised texture, which some customers may not prefer.
- Environmental Concerns: Plastisol inks are made with PVC and contain phthalates, which are considered harmful to the environment. However, eco-friendly alternatives are available.
Water-Based Ink
Water-based inks are popular among eco-conscious screen printers because they are more environmentally friendly than plastisol inks. Water-based inks use water as a solvent, which means they are free of PVC and phthalates. They penetrate the fabric, creating a softer, more natural feel compared to plastisol.
-
Pros:
- Soft Hand: Water-based inks are absorbed into the fabric, resulting in a print that feels soft and smooth to the touch, rather than sitting on top of the fabric.
- Eco-Friendly: Water-based inks are non-toxic and better for the environment, making them a great choice for businesses that prioritize sustainability.
- Breathable Prints: Because the ink is absorbed into the fabric, it allows the fabric to breathe more easily, which is ideal for lightweight garments like t-shirts.
-
Cons:
- Difficult to Cure: Water-based inks require more precise curing conditions, including higher temperatures and proper airflow. If not cured properly, the prints can fade or wash out.
- Limited on Dark Fabrics: Water-based inks are less opaque than plastisol, making them less suitable for printing on dark fabrics unless specialized opaque water-based inks are used.
- Shorter Working Time: Water-based inks dry out more quickly than plastisol, so printers need to work faster or use additives to extend the working time.
Discharge Ink
Discharge ink is a type of water-based ink that works by removing (or "discharging") the dye from the fabric, leaving a soft, natural feel. It’s commonly used for printing on dark fabrics to create a soft, faded look, similar to vintage-style prints.
-
Pros:
- Soft Hand: Like other water-based inks, discharge ink creates a soft, breathable print that feels integrated with the fabric.
- Ideal for Dark Fabrics: Discharge ink removes the dye from dark fabrics, allowing for bright, vivid prints without the need for a heavy underbase layer.
- Versatile Design Options: This ink can be used alone for a washed-out, vintage look, or combined with other inks for more complex designs.
-
Cons:
- Chemical Use: Discharge inks contain chemicals that break down the fabric dye, and while these chemicals are generally safe, some screen printers may prefer to avoid them.
- Color Variability: The effectiveness of discharge ink can vary depending on the fabric and dye used in the garment, resulting in inconsistent colors.
- Curing Complexity: Discharge inks require precise curing conditions, including higher temperatures and specific curing times.
Specialty Inks
Specialty inks can add unique effects to your screen-printed designs, offering creative ways to make your products stand out. These inks are typically more expensive and require special handling, but they can be a great addition to your product offerings.
- Metallic Inks: These inks contain metallic flakes that create a shiny, reflective finish. They are commonly used for adding accents or bold, eye-catching designs.
- Glow-in-the-Dark Inks: These inks absorb light during the day and emit a glow in the dark, making them ideal for novelty items or special event apparel.
- Puff Inks: Puff inks expand when heated, creating a raised, textured effect that adds dimension to the design.
- High-Density Inks: Similar to puff inks, high-density inks create a raised print, but they are denser and more durable, giving the design a 3D effect.
- Glitter Inks: Glitter inks are mixed with tiny glitter particles to add sparkle and shine to the design, perfect for festive or fashionable items.
Choosing the Right Ink for Your Project
When selecting an ink for your screen printing project, consider the following factors:
- Fabric Type: Some inks work better on certain fabrics. For example, water-based inks are ideal for cotton, while plastisol is better suited for polyester or blended fabrics.
- Desired Print Feel: If you want a soft, breathable print, water-based or discharge inks are the best choice. For bolder, more vibrant designs, plastisol may be the way to go.
- Environmental Impact: If sustainability is a priority for your business, opt for water-based or eco-friendly plastisol inks.
- Special Effects: If you’re looking to add something unique to your designs, consider using specialty inks like metallic, glitter, or glow-in-the-dark inks.
5. Squeegees: Choosing the Right One
The squeegee is one of the most important tools in screen printing. It’s responsible for pushing the ink through the screen and onto the substrate, and the type of squeegee you use can have a significant impact on the quality of the print. Squeegees come in different sizes, shapes, and materials, each suited for different types of printing projects.
Squeegee Blade Types
Squeegees are made with different types of blades, and each blade has a specific purpose in the screen printing process.
- Square Blade: The most common type of squeegee blade, a square or flat blade is ideal for standard printing jobs. It applies a consistent amount of ink across the entire design and is suitable for most textiles.
- Rounded Blade: Rounded blades are used for printing thick layers of ink, making them ideal for specialty inks like metallics or puff inks. The rounded edge reduces the amount of ink that’s pushed through the screen, creating a thicker deposit.
- Angled Blade: Angled or beveled blades are often used for printing on uneven or textured surfaces. The angled edge allows for better control over ink application, ensuring a smooth print on challenging surfaces like wood or metal.
Squeegee Blade Materials
The material of the squeegee blade can affect its flexibility and durability, and different materials are suited for different printing applications.
- Rubber: Rubber squeegees are flexible and provide excellent control over ink flow. They are ideal for printing on textiles, as they allow for smooth, even ink application.
- Urethane: Urethane squeegees are more durable and resistant to chemicals than rubber squeegees. They are commonly used in industrial printing applications where the squeegee is exposed to harsh chemicals or solvents.
- Neoprene: Neoprene squeegees offer a balance between flexibility and durability. They are suitable for printing on a variety of substrates, including textiles, paper, and plastics.
Squeegee Durometer
The durometer of a squeegee refers to its hardness, with higher numbers indicating harder blades. Squeegees typically range from 60 to 90 durometer, and the right durometer depends on the type of ink, screen mesh, and substrate you’re using.
- 60 Durometer: A soft blade that’s ideal for printing on rough or uneven surfaces, such as wood or textured textiles. It’s also a good choice for printing with thick, heavy inks.
- 70 Durometer: A medium-hard blade that’s suitable for most standard screen printing applications. It offers a good balance of flexibility and durability, making it a versatile choice for apparel printing.
- 80–90 Durometer: A hard blade that’s best for high-precision printing or for printing with thin, fluid inks. Harder squeegees provide more control over ink deposition and are ideal for fine detail work.
Handle Types
Squeegee handles come in various materials and designs, and the right handle can improve your comfort and control during the printing process.
- Wooden Handles: Wooden squeegee handles are traditional and provide a comfortable, natural grip. They are durable and can be used for long periods without causing strain.
- Aluminum Handles: Aluminum handles are lightweight and easy to clean. They are more durable than wooden handles and are often used in professional screen printing shops.
- Ergonomic Handles: Ergonomic squeegee handles are designed to reduce hand fatigue during long printing sessions. They have contoured shapes that fit comfortably in the hand, making them ideal for high-volume printing.
Maintaining Your Squeegees
Proper maintenance of your squeegees is essential for ensuring high-quality prints and extending the life of your tools. Here are a few tips for keeping your squeegees in top condition:
- Clean Immediately After Use: Always clean your squeegees after each use to prevent ink from drying on the blade. Use a mild solvent or screen cleaner to remove any ink residue.
- Store Flat: Store your squeegees flat or hanging to prevent the blades from warping. Avoid leaning them against surfaces where the blade can be bent or damaged.
- Replace Worn Blades: Over time, squeegee blades can become worn or damaged, leading to uneven prints. Replace your blades when you notice any signs of wear, such as nicks or bends in the edge.
6.Screen Coating and Exposure Units in Screen Printing
In the screen printing process, screen coating and exposure units play a critical role in preparing screens for printing. This section will cover the importance, types, and best practices related to screen coating and exposure units.
1. Understanding Screen Coating
Screen coating involves applying a light-sensitive emulsion onto a screen mesh, creating a stencil for the printing process. This step is essential for achieving precise designs and high-quality prints.
1.1 Importance of Screen Coating
- Precision: Proper screen coating allows for fine details in designs, ensuring accurate reproduction of artwork.
- Durability: A well-coated screen withstands multiple prints without degrading, making it suitable for high-volume jobs.
- Cost Efficiency: High-quality emulsion results in fewer reprints and reduced material waste, improving overall profitability.
1.2 Types of Screen Coatings
- Diazo Emulsion: A popular choice for its versatility and ease of use. It requires a UV light source for exposure and is suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Photopolymer Emulsion: Offers faster exposure times and is more sensitive to light than diazo emulsions, making it ideal for fine details and intricate designs.
- Hybrid Emulsion: Combines the properties of both diazo and photopolymer emulsions, offering a balance of durability and detail.
2. Screen Coating Process
2.1 Preparing the Screen
- Cleaning: Ensure the screen is thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants or residues. A degreaser can be used for optimal results.
- Drying: After cleaning, dry the screen completely to avoid trapping moisture in the emulsion.
2.2 Coating Techniques
- Flood Coating: Pour emulsion onto the screen and spread it evenly using a squeegee. This technique ensures even coverage.
- Single Stroke Coating: Apply emulsion with a single stroke from the top to the bottom of the screen, minimizing the risk of bubbles or uneven layers.
- Dual Coating: Apply a thin layer of emulsion on both sides of the screen for added durability and finer detail.
2.3 Drying the Coated Screen
- Drying Conditions: Allow the coated screen to dry in a dark room to prevent premature exposure. Ensure proper ventilation to expedite drying.
- Drying Time: Depending on the emulsion used, drying times can range from 30 minutes to several hours.
3. Exposure Units: Purpose and Functionality
Exposure units are essential for exposing the coated screen to light, hardening the emulsion in the areas not covered by the design. This creates the stencil that will be used for printing.
3.1 Types of Exposure Units
- UV Exposure Units: Use ultraviolet light to expose the emulsion. They can be either standalone units or built into larger screen printing machines.
- Metal Halide Units: These units provide a more powerful light source and faster exposure times, making them suitable for high-volume production.
- LED Exposure Units: Energy-efficient and long-lasting, LED units are becoming increasingly popular. They provide consistent light output and shorter exposure times.
3.2 Choosing the Right Exposure Unit
- Screen Size Compatibility: Ensure the exposure unit can accommodate the screen sizes you plan to use.
- Light Source Type: Choose a light source that best suits your production needs, considering factors like exposure time and cost.
- Ease of Use: Look for units that offer user-friendly features such as adjustable height and timers.
4. The Exposure Process
4.1 Setting Up the Exposure Unit
- Positioning the Screen: Place the coated screen in the exposure unit, ensuring it is secured and level.
- Film Positive Alignment: Lay the film positive (the design) onto the screen, ensuring proper alignment. Use registration marks for accuracy.
4.2 Exposure Time
- Testing Exposure Times: Each emulsion requires specific exposure times based on the light source used. Conduct tests to determine optimal exposure times for your materials.
- Overexposure vs. Underexposure: Be mindful of exposure times. Overexposure can lead to a loss of detail, while underexposure may result in incomplete stencils.
4.3 Post-Exposure Processing
- Washing Out the Screen: After exposure, rinse the screen with water to remove the unexposed emulsion, revealing the stencil.
- Drying and Curing: Allow the screen to dry completely before use. Some printers prefer to cure the screen in an oven to enhance durability.
5. Best Practices for Screen Coating and Exposure
- Consistent Application: Ensure that emulsion is applied evenly to avoid inconsistencies in print quality.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep exposure units clean and well-maintained to ensure optimal performance.
- Monitor Environmental Conditions: Temperature and humidity can affect the coating and exposure processes. Maintain a controlled environment for best results.
- Conduct Regular Tests: Perform exposure tests periodically to calibrate exposure times and ensure consistent results.
6. Conclusion
Screen coating and exposure units are vital components of the screen printing process. Mastering these techniques ensures high-quality prints and efficient production workflows. By understanding the types of emulsions, proper coating methods, and exposure practices, screen printers can achieve superior results that meet client demands while maintaining profitability. Embracing advancements in technology, such as LED exposure units, can further enhance efficiency and sustainability in the screen printing industry.
7. Chemicals and Cleaners for Screen Maintenance
Proper maintenance of screen printing equipment, particularly screens and squeegees, is crucial for producing high-quality prints and extending the lifespan of your tools. The right chemicals and cleaners can help remove ink, emulsion, and other residues, ensuring your screens are ready for use. This section covers the types of cleaners, their applications, and best practices for screen maintenance.
Types of Chemicals and Cleaners
-
Screen Opener/Ink Remover
- Description: Screen openers or ink removers are solvents designed to dissolve and remove ink from screens, squeegees, and other printing equipment.
-
Uses:
- Cleaning Wet Inks: Effective for cleaning wet plastisol, water-based, and specialty inks from screens immediately after printing.
- Pre-press Preparation: Used before coating screens with emulsion to ensure a clean surface.
- Application: Apply the screen opener to the affected areas and scrub gently with a soft cloth or sponge. Rinse thoroughly with water.
-
Emulsion Remover
- Description: Emulsion removers are specially formulated to dissolve the photo-sensitive emulsion used to create stencils on screens.
-
Uses:
- Reclaiming Screens: Essential for cleaning screens after the printing process to reuse them for new designs.
- Effective Stencil Removal: Ensures complete removal of emulsion without damaging the screen mesh.
- Application: Spray or apply the emulsion remover onto the screen and allow it to sit for a specified time (usually a few minutes). Use a pressure washer or hose to rinse off the emulsion thoroughly.
-
Squeegee Cleaner
- Description: Squeegee cleaners are designed to remove ink and residue from squeegees, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
-
Uses:
- Prevent Ink Build-Up: Regular cleaning of squeegees after each print run prevents ink from drying and sticking.
- Maintaining Print Quality: Keeps squeegees clean, allowing for consistent ink application.
- Application: Apply the squeegee cleaner to the blade and handle. Wipe with a cloth or sponge, ensuring all ink is removed.
-
Screen Degreaser
- Description: Degreasers are chemicals designed to remove oils, dirt, and grease from the screen surface before coating with emulsion.
-
Uses:
- Pre-Coating Preparation: Ensures a clean and grease-free surface for better emulsion adhesion.
- Removing Fingerprints and Residues: Effective for cleaning screens that have accumulated dirt during handling.
- Application: Spray the degreaser onto the screen and wipe with a lint-free cloth or paper towel.
-
Screen Rinse
- Description: Screen rinses are used to remove leftover chemicals and residues from screens after cleaning.
-
Uses:
- Final Rinse: Ensures that no harmful chemicals remain on the screen that could affect future prints.
- Maintaining Screen Integrity: Helps maintain the mesh and prevents degradation from chemical exposure.
- Application: Use a gentle spray to rinse the screen thoroughly after cleaning.
Best Practices for Screen Maintenance
-
Clean Immediately After Use
- The sooner you clean screens and squeegees after printing, the easier it will be to remove inks and emulsion. Dried inks can be challenging to clean and may require harsher chemicals, which can damage screens.
-
Use Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- When working with chemicals, always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and a mask if necessary. Many cleaners have strong fumes that can be harmful if inhaled.
-
Follow Manufacturer Instructions
- Always read and follow the instructions provided by the chemical manufacturers. They will give guidelines on application methods, dwell times, and safety precautions.
-
Ventilate Your Workspace
- Ensure that your work area is well-ventilated when using cleaners and chemicals. Proper ventilation reduces exposure to harmful fumes and improves safety.
-
Store Chemicals Properly
- Store all cleaning chemicals in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Ensure that all containers are tightly sealed to prevent leaks and contamination.
-
Keep a Cleaning Schedule
- Establish a routine for cleaning and maintaining screens and equipment. Regular maintenance will prolong the life of your screens and improve print quality.
-
Test Before Full Application
- If you're using a new cleaner, test it on a small, inconspicuous area of the screen first to ensure it doesn't damage the mesh or coating.
-
Consider Eco-Friendly Options
- If environmental sustainability is a priority for your business, consider using eco-friendly cleaners and chemicals that minimize environmental impact while still being effective.
By employing the right chemicals and following best practices for screen maintenance, you can enhance your screen printing quality, extend the life of your equipment, and maintain a clean and safe workspace. Proper maintenance not only saves costs in the long run but also ensures consistent, high-quality prints for your clients.
If you'd like to add more information or dive deeper into any specific areas, just let me know!
8. Heat Transfer and Curing Equipment
Heat transfer and curing are critical processes in screen printing, especially when using certain types of inks. Proper curing ensures that inks adhere correctly to the substrate, providing durability and wash resistance. This section covers various types of heat transfer and curing equipment, their applications, and best practices.
Types of Heat Transfer Equipment
-
Heat Press Machines
-
Description: Heat press machines apply heat and pressure to transfer designs from transfer paper or vinyl to substrates like textiles or ceramics.
-
Types:
- Clamshell Heat Press: Features a top plate that opens like a clamshell, ideal for small to medium-sized transfers.
- Swing-Away Heat Press: The upper plate swings away from the lower plate, allowing for easy access and preventing accidental contact with the heated surface.
- Multi-Function Heat Press: Combines heat pressing, cap pressing, and mug pressing capabilities in one machine for versatile applications.
-
Applications: Commonly used for transferring graphics to T-shirts, hats, bags, and other promotional items. Heat presses are especially effective for sublimation and vinyl heat transfer processes.
-
-
Flash Dryers
- Description: Flash dryers use infrared heat to quickly cure inks on the surface of a substrate, allowing for immediate reprinting and reducing ink smudging.
-
Applications:
- Used to cure water-based inks or discharge inks temporarily before applying additional colors.
- Essential for high-volume production environments where speed is crucial.
-
Conveyor Dryers
-
Description: Conveyor dryers consist of a conveyor belt that moves printed items through a heated chamber, curing the ink as it passes.
-
Types:
- Electric Conveyor Dryers: Operate using electric heating elements, ideal for small to medium-sized operations.
- Gas Conveyor Dryers: Use gas as a heat source, providing faster drying times and energy efficiency for larger operations.
-
Applications: Suitable for curing plastisol inks, ensuring a consistent temperature throughout the drying process. Conveyor dryers are ideal for large-scale production, allowing for continuous printing.
-
-
Heat Guns
- Description: Heat guns are handheld devices that blow hot air, used for spot curing or heating specific areas.
-
Applications:
- Often used to quickly cure small areas of ink or vinyl.
- Helpful for removing wrinkles or imperfections from printed garments before finalizing the print.
Curing Equipment for Screen Printing Inks
-
Curing Ovens
- Description: Curing ovens provide a controlled environment for curing screen printed items, ensuring even heat distribution.
- Applications: Ideal for curing specialty inks that require specific temperatures and dwell times. These ovens can handle larger batches and are suitable for various substrates.
-
Infrared Dryers
- Description: Infrared dryers use infrared radiation to cure inks, providing quick drying without contact.
- Applications: Effective for various ink types, including plastisol and water-based inks, and suitable for high-speed production settings.
Importance of Curing in Screen Printing
-
Adhesion and Durability
- Proper curing ensures that the ink adheres well to the substrate, preventing peeling, cracking, or fading over time. Inadequate curing can lead to wash-out or wear of the print.
-
Print Quality
- Curing also affects the overall print quality. Well-cured inks will maintain their vibrant colors and sharp details, while improperly cured inks may appear dull or distorted.
-
Production Efficiency
- Efficient curing processes allow for faster production times. For example, using a conveyor dryer can speed up curing, enabling quicker turnaround for high-volume orders.
-
Compliance with Industry Standards
- Many industries have specific requirements for the durability and washability of printed materials. Proper curing helps meet these standards, ensuring products are suitable for retail and consumer use.
Best Practices for Using Heat Transfer and Curing Equipment
-
Monitor Temperature and Time
- Always follow the manufacturer's recommendations for temperature and curing time. Inadequate curing can result in poor print durability, while over-curing can damage the substrate or ink.
-
Conduct Test Runs
- Before committing to a large run, perform test prints to ensure optimal curing settings. This practice helps identify the right temperature and dwell time for your specific inks and substrates.
-
Regular Maintenance
- Regularly clean and maintain heat transfer and curing equipment to ensure consistent performance. Check for wear and tear, and replace any worn components as needed.
-
Use Quality Inks and Transfers
- Invest in high-quality inks and transfer materials to ensure better adhesion and durability. Quality products will yield better results and reduce the need for reprints.
-
Evaluate the Workspace Environment
- Ensure that the workspace is adequately ventilated, especially when using curing ovens or dryers. This practice helps maintain a safe and comfortable working environment.
-
Educate Staff on Equipment Use
- Provide training for staff on the proper use and maintenance of heat transfer and curing equipment. Well-informed operators can better troubleshoot issues and maintain quality standards.
By understanding the various heat transfer and curing equipment available in screen printing, businesses can ensure high-quality prints that meet customer expectations. Proper curing not only enhances the durability of prints but also contributes to overall production efficiency and quality.
If you have any further questions or would like to expand on a specific area, feel free to ask!
9. Printing Accessories and Tools
Screen printing is a multifaceted process that requires a variety of accessories and tools to achieve high-quality prints. From tools for preparing screens to those used in the printing process and post-printing finishing, each accessory plays a vital role in the overall quality and efficiency of the printing operation. This section highlights essential printing accessories and tools, their applications, and best practices for use.
1. Squeegees
- Description: Squeegees are essential tools in the screen printing process, used to push ink through the stencil on the screen onto the substrate.
-
Types:
- Rubber Squeegees: Commonly used for plastisol inks; they provide good ink coverage and durability.
- Polyurethane Squeegees: Ideal for water-based inks due to their flexibility and ink release properties.
-
Applications:
- Used in various printing applications, including T-shirts, posters, and textiles.
-
Best Practices:
- Choose the appropriate squeegee hardness based on the ink type and substrate.
- Clean squeegees immediately after use to prevent ink from drying on the blade.
2. Screens
- Description: Screens consist of a mesh fabric stretched over a frame, coated with a light-sensitive emulsion to create a stencil for printing.
-
Types:
- Aluminum Frames: Lightweight and durable, ideal for professional setups.
- Wooden Frames: More affordable and suitable for smaller operations or DIY projects.
-
Applications:
- Used for printing a wide range of designs on various substrates.
-
Best Practices:
- Store screens vertically to prevent warping.
- Clean screens thoroughly after each use to maintain print quality and prolong lifespan.
3. Emulsions and Coatings
- Description: Emulsions are light-sensitive substances used to create stencils on screens, while coatings are applied to enhance screen durability and functionality.
-
Types:
- Photopolymer Emulsion: Commonly used for detailed designs and fine lines.
- Capillary Films: Pre-coated films that simplify the screen preparation process.
-
Applications:
- Used for creating stencils for various printing applications.
-
Best Practices:
- Follow manufacturer instructions for application and exposure times.
- Store emulsions in a cool, dark place to prolong shelf life.
4. Ink
- Description: Inks are specially formulated liquids used for screen printing, available in various types to suit different substrates and printing techniques.
-
Types:
- Plastisol Inks: Oil-based inks that provide excellent opacity and durability.
- Water-Based Inks: Eco-friendly inks that are easier to clean but require proper curing.
- Discharge Inks: Used for printing on dark fabrics, these inks bleach the dye of the garment to create a print.
-
Applications:
- Suitable for printing on textiles, plastics, paper, and other materials.
-
Best Practices:
- Use inks that are compatible with the substrate and curing method.
- Keep ink containers sealed to prevent drying.
5. Film and Transparency Sheets
- Description: Film and transparency sheets are used to create positives for exposure onto screens.
-
Types:
- Inkjet Transparency Film: Designed for inkjet printers, offering high-resolution output for detailed designs.
- Laser Transparency Film: Suitable for laser printers, providing crisp lines and vibrant colors.
-
Applications:
- Used for creating stencils for screen exposure.
-
Best Practices:
- Ensure the film is printed at the correct resolution for best results.
- Store unused film in a cool, dry place to avoid damage.
6. Exposure Units
- Description: Exposure units are used to expose screens coated with emulsion using UV light.
-
Types:
- Traditional Exposure Units: Use UV lamps and a vacuum to ensure contact between the film and screen.
- LED Exposure Units: More energy-efficient and provide faster exposure times.
-
Applications:
- Essential for transferring designs onto screens during the preparation phase.
-
Best Practices:
- Regularly clean the glass surface to prevent imperfections in the exposure process.
- Test exposure times with various emulsion types for optimal results.
7. Washout Booth
- Description: A washout booth is a designated area for rinsing out screens after exposure, typically equipped with a spray nozzle and drainage.
-
Applications:
- Used to remove unexposed emulsion and clean screens after printing.
-
Best Practices:
- Ensure proper ventilation in the washout area to manage chemical fumes.
- Regularly maintain the spray system to prevent clogging.
8. Heat Guns
- Description: Heat guns are handheld devices that blow hot air and can be used for spot curing or drying certain inks.
-
Applications:
- Useful for quickly curing small areas or drying prints before further processing.
-
Best Practices:
- Keep the heat gun moving to avoid damaging the substrate or ink.
- Use on low settings for sensitive materials.
9. Pallets
- Description: Pallets provide a stable surface for printing and ensure even pressure during the screen printing process.
-
Types:
- Wooden Pallets: Traditional and durable for most applications.
- Plastic Pallets: Lightweight and easy to clean, suitable for water-based inks.
-
Applications:
- Used for T-shirts, tote bags, and various flat items.
-
Best Practices:
- Ensure pallets are clean and free from debris before printing.
- Use adhesive spray if necessary to keep substrates in place.
10. Measuring and Mixing Tools
- Description: Tools such as scales, mixing cups, and spatulas are essential for measuring and mixing inks and other chemicals.
-
Applications:
- Used to ensure accurate ink mixtures for color consistency and desired properties.
-
Best Practices:
- Use dedicated tools for different inks to prevent cross-contamination.
- Keep mixing area clean to maintain ink integrity.
Conclusion
The right printing accessories and tools are fundamental to achieving high-quality results in screen printing. By understanding the purpose and best practices for each accessory, screen printers can enhance their workflow, improve print quality, and ultimately satisfy their customers. Regular maintenance and proper usage of these tools will lead to better efficiency and longer equipment lifespan.
If you have any further questions or would like to expand on specific accessories or tools, feel free to ask!
10. Blank Apparel and Textiles for Screen Printing
Blank apparel and textiles serve as the canvas for screen printing, making the selection of the right materials crucial for achieving high-quality, durable prints. This section explores the various types of blank apparel and textiles available, their benefits, and key factors to consider when choosing materials for screen printing.
1. Types of Blank Apparel
-
T-Shirts
- Description: The most popular and versatile option for screen printing, available in various styles, colors, and materials.
-
Fabric Types:
- Cotton: Soft, breathable, and easy to print on. It absorbs ink well, making it ideal for vibrant designs.
- Polyester: Durable and resistant to shrinking and fading, often used for athletic wear. Works well with dye-sublimation printing.
- Blends (Cotton/Polyester): Combine the best features of both fabrics, providing comfort and durability.
- Applications: Suitable for promotional events, merchandise, team uniforms, and casual wear.
-
Hoodies and Sweatshirts
- Description: Comfortable apparel perfect for cooler weather, providing larger print areas for designs.
-
Fabric Types:
- Fleece: Soft and warm, ideal for casual wear. Usually made from cotton or polyester.
- French Terry: Lightweight and breathable, offering a smooth surface for printing.
- Applications: Popular for schools, sports teams, and custom merchandise.
-
Caps and Hats
- Description: Headwear provides a unique surface for branding and promotional designs.
-
Fabric Types:
- Cotton Twill: Durable and commonly used for baseball caps and visors.
- Polyester: Often used for moisture-wicking properties in athletic caps.
- Applications: Great for outdoor events, sports teams, and corporate branding.
-
Bags and Totes
- Description: Blank bags, including tote bags and drawstring bags, are practical items for branding and promotional purposes.
-
Fabric Types:
- Canvas: Durable and strong, ideal for heavy-duty usage and holds up well to printing.
- Non-Woven Polypropylene: Lightweight and eco-friendly, commonly used for shopping bags.
- Applications: Ideal for trade shows, giveaways, and retail merchandise.
-
Activewear
- Description: Apparel designed for sports and physical activities, often featuring moisture-wicking technology.
-
Fabric Types:
- Polyester and Spandex Blends: Provide stretch and breathability, suitable for athletic use.
- Nylon: Lightweight and strong, often used in performance apparel.
- Applications: Perfect for gyms, sports teams, and outdoor activities.
-
Workwear
- Description: Durable clothing designed for occupational use, such as uniforms and safety apparel.
-
Fabric Types:
- Cotton/Polyester Blends: Offer comfort and resistance to wear.
- High-Visibility Fabrics: Used for safety apparel, often in bright colors with reflective elements.
- Applications: Used in various industries, including construction, hospitality, and healthcare.
2. Considerations for Selecting Blank Apparel and Textiles
-
Fabric Composition
- The type of fabric significantly affects print quality, durability, and feel. Cotton is generally the easiest to print on, while polyester requires specific inks and processes for optimal results.
-
Print Method Compatibility
- Different fabrics may work better with certain printing techniques. For instance, plastisol inks work well on cotton, while dye-sublimation is ideal for polyester. It’s crucial to match the fabric with the intended printing method.
-
Color and Style Variety
- Availability in various colors and styles allows for creative flexibility. Lighter fabrics are better for vibrant ink colors, while darker fabrics may require special inks for visibility.
-
Sizing and Fit
- Consider the target audience when selecting sizes and fits. Offering a range of sizes ensures inclusivity and customer satisfaction.
-
Sustainability
- Increasingly, consumers are looking for eco-friendly options. Blank apparel made from organic cotton, recycled materials, or water-based inks can appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
-
Cost-Effectiveness
- While quality is essential, the cost of blank apparel can significantly impact overall pricing. Balancing quality with affordability is vital for successful screen printing businesses.
-
Supplier Reliability
- Choose reputable suppliers known for quality and consistency. This ensures that the blank apparel meets the required standards and reduces the risk of defects during printing.
3. Benefits of Using Quality Blank Apparel
-
Enhanced Print Quality
- High-quality fabrics provide better ink adhesion, resulting in sharper and more vibrant prints.
-
Increased Durability
- Well-made garments withstand washing and wear, prolonging the life of the printed designs.
-
Customer Satisfaction
- Offering quality products leads to higher customer satisfaction, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth.
-
Brand Image
- Providing high-quality blank apparel enhances the overall brand image, reflecting a commitment to quality and customer care.
-
Versatility
- Blank apparel can be used in various markets, including retail, corporate, promotional, and custom designs, increasing sales opportunities.
Conclusion
Selecting the right blank apparel and textiles is crucial for achieving high-quality results in screen printing. By understanding the different types of apparel, their applications, and key considerations for selection, screen printers can ensure they provide durable and appealing products that meet customer needs. Quality blank apparel not only enhances print results but also contributes to overall business success.
If you have further questions or would like to expand on a specific area regarding blank apparel and textiles, feel free to ask!
11. Design Tools and Software for Screen Printing
Effective design is crucial for successful screen printing, as it determines the quality and impact of the final printed product. A variety of design tools and software are available to help artists and printers create stunning visuals that can be effectively reproduced on various substrates. This section discusses popular design tools and software for screen printing, their features, applications, and best practices.
1. Graphic Design Software
-
Adobe Illustrator
- Description: A vector graphics editor widely used for creating logos, illustrations, and complex designs.
-
Key Features:
- Powerful drawing tools for creating scalable vector graphics.
- Advanced typography features for manipulating text.
- Extensive color management options for accurate color representation.
-
Applications:
- Ideal for creating designs that need to be resized without loss of quality, such as logos and intricate artwork.
-
Best Practices:
- Use layers to organize design elements for easy editing.
- Save files in vector format (like .AI or .EPS) for optimal print quality.
-
CorelDRAW
- Description: Another popular vector graphic design software used for creating detailed artwork and layouts.
-
Key Features:
- Intuitive interface for beginners and advanced users.
- Robust tools for color management, text manipulation, and image editing.
-
Applications:
- Suitable for producing designs for screen printing, engraving, and sign-making.
-
Best Practices:
- Utilize the "PowerClip" feature to easily place objects within other shapes.
- Export files in formats compatible with screen printing equipment (like .CDR, .EPS).
-
Inkscape
- Description: A free and open-source vector graphics editor.
-
Key Features:
- Comprehensive drawing tools and support for various file formats.
- Ability to create intricate designs without software costs.
-
Applications:
- Great for individuals or small businesses looking to create designs for screen printing on a budget.
-
Best Practices:
- Regularly save your work, as software may experience bugs.
- Familiarize yourself with the user community for tips and resources.
2. Color Separation Software
-
Separation Studio
- Description: Specialized software designed for color separation in screen printing.
-
Key Features:
- Automatic color separation for multi-color designs.
- Tools for adjusting halftones and optimizing color output.
-
Applications:
- Used primarily by screen printers to prepare artwork for the printing process.
-
Best Practices:
- Double-check color separations for accuracy before sending to print.
- Experiment with different settings to achieve the desired print quality.
-
AccuRIP
- Description: Software designed for creating high-quality film positives for screen exposure.
-
Key Features:
- Simplifies the process of printing film positives for color-separated artwork.
- Supports various printers and media types.
-
Applications:
- Essential for screen printing businesses that require precise film for exposure.
-
Best Practices:
- Use high-quality film and settings for the best results.
- Regularly update the software to access new features and improvements.
3. Mockup and Visualization Tools
-
Placeit
- Description: An online mockup generator that allows users to visualize designs on various products.
-
Key Features:
- Extensive library of product templates (T-shirts, hoodies, bags, etc.).
- User-friendly interface for quick mockup creation.
-
Applications:
- Useful for marketing and showcasing designs to clients before production.
-
Best Practices:
- Use high-resolution images for a professional appearance.
- Share mockups with clients for feedback and approval before printing.
-
Smartmockups
- Description: A tool for creating realistic mockups for branding and marketing purposes.
-
Key Features:
- Integration with graphic design software for easy uploads.
- Variety of mockup styles for apparel, packaging, and more.
-
Applications:
- Ideal for promoting designs on social media, websites, or in presentations.
-
Best Practices:
- Experiment with different backgrounds and settings to enhance product appeal.
- Use mockups in marketing materials to attract potential customers.
4. Typography and Font Management
-
FontForge
- Description: A free font editing software that allows users to create and edit fonts.
-
Key Features:
- Open-source with robust capabilities for font design and editing.
- Supports various font formats for compatibility.
-
Applications:
- Useful for custom typography creation for screen printing designs.
-
Best Practices:
- Experiment with different font styles to create unique designs.
- Regularly back up font files to prevent data loss.
-
WhatTheFont
- Description: An online tool for identifying fonts from images.
-
Key Features:
- Quickly identifies fonts used in existing designs.
- Offers similar font suggestions for design inspiration.
-
Applications:
- Helps screen printers find or create similar fonts for their designs.
-
Best Practices:
- Upload clear images of text for accurate identification.
- Explore suggested alternatives for diverse design options.
5. Collaboration and Project Management Tools
-
Trello
- Description: A project management tool that uses boards and cards to organize tasks.
-
Key Features:
- Customizable boards for tracking design projects and workflows.
- Collaboration features for teams to communicate and share ideas.
-
Applications:
- Useful for managing design projects and coordinating with clients or team members.
-
Best Practices:
- Use labels and due dates to keep projects on track.
- Regularly update boards to reflect project progress.
-
Slack
- Description: A communication platform for team collaboration.
-
Key Features:
- Channels for organizing discussions by project or topic.
- Integration with other design tools for seamless workflow.
-
Applications:
- Facilitates communication between designers, clients, and production teams.
-
Best Practices:
- Create dedicated channels for specific projects to keep conversations organized.
- Utilize integrations with design tools to streamline processes.
Conclusion
The right design tools and software are essential for producing high-quality screen printing designs. From graphic design software to color separation tools and collaboration platforms, each tool plays a unique role in enhancing the design process. By understanding the functionalities and applications of these tools, screen printers can improve their workflow, enhance creativity, and deliver outstanding results to their clients.
If you have any further questions or would like to delve deeper into any specific tools or software, feel free to ask!
12. Specialized Screen Printing Tools and Supplies
Screen printing involves a range of specialized tools and supplies that enhance the quality and efficiency of the printing process. From screens and squeegees to exposure units and inks, each tool plays a critical role in achieving high-quality prints. This section outlines the essential specialized tools and supplies used in screen printing, their functions, and considerations for use.
1. Screens and Frames
-
Screens
- Description: Mesh fabric stretched over a frame used to transfer ink onto the substrate. The mesh size determines the amount of ink that passes through.
-
Types:
- Monofilament Screens: Made from single strands of polyester; offers precision and durability.
- Multifilament Screens: Composed of multiple strands, providing greater ink flow but less detail.
-
Considerations:
- Choose the appropriate mesh count (measured in threads per inch) based on the detail of the design. Higher mesh counts are better for fine details, while lower counts are ideal for bold designs.
-
Frames
- Description: The structure that holds the screen in place, often made from wood or aluminum.
-
Types:
- Wood Frames: Economical but less durable; suitable for smaller shops.
- Aluminum Frames: Lightweight, durable, and compatible with a range of screen types.
-
Considerations:
- Ensure frames are properly tensioned to prevent distortion during printing.
2. Squeegees
- Description: A rubber blade attached to a handle, used to push ink through the screen onto the substrate.
-
Types:
- Standard Squeegees: Basic design with a single blade for general use.
- Durometer Squeegees: Offer varying hardness levels for different ink types and print techniques (e.g., soft for thicker inks, hard for finer lines).
-
Considerations:
- Choose the appropriate squeegee size and durometer based on the design and substrate to ensure optimal ink transfer.
3. Exposure Units
- Description: Equipment used to expose photo emulsion on screens, allowing for the creation of stencils.
-
Types:
- Fluorescent Exposure Units: Cost-effective, but may require longer exposure times.
- Metal Halide Exposure Units: Provide faster exposure times and more even light distribution.
-
Considerations:
- Ensure the exposure unit has the correct wattage and bulb type for the emulsion being used.
4. Inks
-
Plastisol Inks
- Description: PVC-based inks known for their opacity and versatility.
- Applications: Ideal for a wide range of fabrics, especially cotton and blends.
- Considerations: Requires curing at high temperatures to set properly.
-
Water-Based Inks
- Description: Eco-friendly inks made from water and pigments.
- Applications: Best for lightweight fabrics and achieving a softer feel.
- Considerations: Requires proper moisture control during printing and curing.
-
Discharge Inks
- Description: Inks that remove dye from colored fabrics, leaving a soft print.
- Applications: Ideal for achieving a vintage look on dark fabrics.
- Considerations: Requires specific handling and curing techniques.
5. Emulsion and Coating Supplies
- Description: Light-sensitive materials used to create stencils on screens.
-
Types:
- Photo Emulsions: Used for exposure; sensitive to UV light.
- Capillary Films: Pre-coated film that simplifies the process of screen preparation.
-
Considerations:
- Follow manufacturer instructions for coating and exposure times to ensure accurate stencil creation.
6. Washout Stations
- Description: Dedicated areas or equipment for rinsing screens after exposure.
-
Features:
- Equipped with water sprayers, drains, and adequate lighting for the rinsing process.
-
Considerations:
- Ensure proper drainage and safety measures to handle chemicals used in emulsion removal.
7. Heat Press Machines
- Description: Equipment used for applying heat and pressure to transfer designs onto substrates.
-
Types:
- Clamshell Heat Presses: Open like a clamshell; easy to use for flat items.
- Swing-Away Heat Presses: Swing to the side for easier access; better for thicker items.
-
Considerations:
- Choose the right temperature and pressure settings based on the substrate and transfer material.
8. Cleaning Supplies
- Description: Tools and chemicals used to maintain screens, squeegees, and other equipment.
-
Types:
- Screen Cleaners: Solvents or detergents for removing ink and emulsion from screens.
- Squeegee Cleaners: Specific formulations designed to clean and preserve squeegee blades.
-
Considerations:
- Use environmentally friendly cleaners where possible to minimize waste and pollution.
9. Miscellaneous Supplies
- Description: Other essential supplies that enhance the screen printing process.
-
Examples:
- Tape: Used to block off areas of the screen or hold substrates in place.
- Ink Cups: Containers for holding and mixing ink during printing.
- Test Swatches: Small fabric samples for testing ink and print quality.
-
Considerations:
- Maintain a well-stocked inventory of miscellaneous supplies to streamline the printing process.
Conclusion
Specialized tools and supplies are essential for successful screen printing. Each tool serves a specific purpose, from preparing screens to applying inks and cleaning equipment. Understanding the functionality and applications of these tools allows screen printers to enhance their workflow, achieve high-quality prints, and maintain their equipment effectively. Investing in quality tools and supplies ultimately contributes to the overall success of a screen printing business.
If you have any questions or would like to explore a specific area further, feel free to ask!
13. Advanced Techniques and Customization Options
Screen printing is a versatile method that offers numerous advanced techniques and customization options. These innovations allow printers to create intricate designs, achieve specific effects, and cater to a broader range of products and markets. This section outlines some of the most popular advanced techniques and customization options in screen printing, their applications, and considerations for use.
1. Color Mixing and Custom Inks
-
Color Mixing
- Description: The process of combining different inks to create custom colors that match specific requirements.
-
Techniques:
- Pantone Matching System (PMS): A standardized color matching system used to ensure color consistency across various prints.
- CMYK Color Mixing: Utilizing the four-color printing process (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key/Black) to create a wide range of colors.
-
Considerations:
- Maintain a color mixing chart for reference.
- Conduct test prints to verify color accuracy before final production.
-
Custom Inks
- Description: Specialty inks that provide unique effects and finishes.
-
Types:
- Metallic Inks: Inks that contain metallic particles, giving a shiny or reflective finish.
- Fluorescent Inks: Bright, vivid inks that glow under UV light, ideal for promotional items and events.
- Glow-in-the-Dark Inks: Inks that absorb light and emit it in darkness, creating eye-catching designs.
-
Considerations:
- Test custom inks on different substrates to ensure compatibility and performance.
2. Specialty Printing Techniques
-
Simulated Process Printing
- Description: A technique that uses halftones and a limited color palette to simulate full-color images.
-
Applications:
- Ideal for printing photographic images and complex graphics with a limited number of screens.
-
Considerations:
- Requires a deep understanding of color theory and halftoning techniques to achieve realistic results.
-
Spot Color Printing
- Description: The use of specific, pre-mixed inks to produce solid colors in designs.
-
Applications:
- Commonly used for logos and designs requiring precise color matching.
-
Considerations:
- Choose colors from a PMS guide to ensure accuracy and consistency.
-
4-Color Process Printing
- Description: A printing technique that combines four base colors (CMYK) to create a full spectrum of colors.
-
Applications:
- Used for designs with gradients, photographs, or complex images.
-
Considerations:
- Ensure proper registration to maintain alignment between the different color layers.
3. Layering Techniques
-
Underbase Printing
- Description: A technique where a white or light-colored base layer is printed first, allowing darker inks to appear more vibrant.
-
Applications:
- Essential for printing on dark fabrics to enhance the visibility of colors.
-
Considerations:
- Proper curing of the underbase is critical to prevent bleed-through from subsequent layers.
-
Overprinting
- Description: Printing additional colors over previously printed layers to create depth and texture.
-
Applications:
- Useful for adding highlights or shadows to designs.
-
Considerations:
- Experiment with transparency and ink viscosity for desired effects.
-
Discharge Printing
- Description: A method that uses discharge inks to remove dye from colored fabrics, resulting in a soft print.
-
Applications:
- Popular for achieving vintage or distressed looks on dark fabrics.
-
Considerations:
- Requires specific handling and curing techniques to ensure effective dye removal.
4. Customization Options
-
Personalization
- Description: Adding unique names, numbers, or designs to garments for individual customers.
-
Applications:
- Ideal for sports uniforms, event merchandise, or promotional items.
-
Considerations:
- Use digital printing methods or heat transfer for accurate personalization.
-
Specialty Substrates
- Description: Printing on non-traditional materials and substrates.
-
Examples:
- Wood: Creating designs on wooden surfaces for rustic products.
- Metal: Utilizing screen printing on metal surfaces for signage and décor.
- Plastics: Printing on various plastic materials for promotional items or packaging.
-
Considerations:
- Choose appropriate inks and curing methods based on substrate characteristics.
-
Textural Effects
- Description: Incorporating textures into prints for added visual and tactile interest.
-
Techniques:
- Puff Inks: Inks that expand when heated, creating a raised effect.
- Foil Printing: Applying metallic foil to designs for a shiny finish.
-
Considerations:
- Experiment with different combinations of inks and techniques to achieve desired textures.
5. Eco-Friendly Options
-
Water-Based Inks
- Description: Eco-friendly inks that are made from water and pigments, reducing harmful emissions.
-
Applications:
- Ideal for sustainable clothing lines and brands focusing on environmental responsibility.
-
Considerations:
- Requires careful handling to prevent drying and clogging during the printing process.
-
Biodegradable Materials
- Description: Using eco-friendly substrates and inks that break down naturally over time.
-
Applications:
- Popular among brands promoting sustainability.
-
Considerations:
- Verify the performance of biodegradable inks and substrates during the printing process.
Conclusion
Advanced techniques and customization options in screen printing allow businesses to differentiate themselves and offer unique products to their clients. From color mixing and specialty inks to personalized designs and eco-friendly options, these innovations enhance creativity and expand the possibilities of screen printing. By understanding and mastering these techniques, printers can elevate their work, attract a wider customer base, and stay competitive in the market.
If you have any specific questions or would like to dive deeper into any of these techniques, feel free to ask!
14. Common Challenges and Solutions in Screen Printing
Screen printing is a popular method for producing high-quality designs on various substrates, but it comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges and their solutions can help printers improve their workflow, reduce errors, and achieve better results. This section outlines some of the most common challenges encountered in screen printing and provides practical solutions.
1. Registration Issues
Challenge: Achieving proper alignment of multiple colors during the printing process can be difficult, especially when using multiple screens.
Solutions:
- Use Registration Marks: Incorporate registration marks in the design to ensure accurate alignment of each screen.
- Adjust the Press Setup: Regularly check and calibrate the screen printing press to maintain proper registration.
- Invest in a High-Quality Press: Use a press that offers precise registration adjustments, such as micro-registration capabilities.
2. Ink Bleeding and Smudging
Challenge: Ink bleeding occurs when the ink spreads beyond the intended area, resulting in a blurred or fuzzy design.
Solutions:
- Choose the Right Mesh Count: Use a finer mesh for detailed designs to limit ink flow and reduce bleeding.
- Control Ink Viscosity: Adjust the ink’s viscosity by adding a reducer or thickener as needed to ensure proper flow.
- Use Flash Dryers: Flash drying between colors can help set the ink and prevent smudging during the printing process.
3. Screen Clogging
Challenge: Clogging occurs when ink dries in the mesh, preventing proper ink flow and ruining prints.
Solutions:
- Use Proper Emulsion: Select an emulsion that is compatible with the ink being used to prevent premature drying.
- Keep Screens Clean: Regularly clean screens and squeegees immediately after use to avoid buildup.
- Implement a Proper Washout Process: Ensure that screens are rinsed thoroughly after exposure to remove any residual emulsion.
4. Ink Drying on Screens
Challenge: Ink can dry on the screen during the printing process, especially in warm environments, leading to blockages.
Solutions:
- Maintain Optimal Working Conditions: Keep the workspace cool and humid to slow down drying times.
- Use Retarder Additives: Add a retarder to the ink to extend its working time and prevent drying on the screen.
- Cover Inks: Use a damp cloth or plastic wrap to cover unused ink on screens during breaks to keep it wet.
5. Inconsistent Print Quality
Challenge: Variability in print quality can arise from various factors, leading to unsatisfactory results.
Solutions:
- Standardize Processes: Develop a standardized workflow that includes detailed documentation of each step in the printing process.
- Conduct Regular Maintenance: Regularly maintain and calibrate equipment to ensure optimal performance and consistent results.
- Conduct Test Prints: Always run test prints before full production to identify any potential issues.
6. Substrate Compatibility Issues
Challenge: Not all inks work well with every substrate, leading to poor adhesion or washability.
Solutions:
- Conduct Adhesion Tests: Test ink and substrate combinations before full-scale printing to ensure compatibility.
- Use Specialty Inks: Opt for inks designed specifically for the substrate being printed, such as water-based inks for cotton or discharge inks for dark fabrics.
- Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Always adhere to the ink and substrate manufacturer's guidelines for best results.
7. Environmental Factors
Challenge: Factors such as humidity and temperature can impact the printing process, affecting ink drying times and overall quality.
Solutions:
- Monitor Environmental Conditions: Use hygrometers and thermometers to track humidity and temperature in the workspace.
- Implement Climate Control: Consider installing air conditioning or dehumidifiers to maintain a stable printing environment.
- Adjust Ink Formulation: Modify ink formulations based on environmental conditions, using additives that enhance performance in specific climates.
8. Equipment Breakdowns
Challenge: Equipment failures can halt production and lead to delays.
Solutions:
- Conduct Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine maintenance for all equipment to identify and address issues before they lead to breakdowns.
- Keep Spare Parts on Hand: Maintain an inventory of essential spare parts to minimize downtime in case of equipment failure.
- Invest in Quality Equipment: Choose reliable and durable equipment that is less prone to breakdowns.
Conclusion
Screen printing is a rewarding yet complex process that comes with its own set of challenges. By understanding these challenges and implementing practical solutions, printers can improve their workflow, reduce errors, and achieve consistent, high-quality results. Continuous learning, regular maintenance, and a proactive approach to problem-solving are key to success in the screen printing industry.
If you have any specific challenges you’re facing or would like to discuss further solutions, feel free to ask!
15. Conclusion: Building Your Screen Printing Business
Building a successful screen printing business requires a combination of technical expertise, creative vision, and strategic planning. As the industry continues to evolve, staying informed about new technologies, trends, and customer preferences is crucial. This conclusion synthesizes the key components discussed throughout this guide and provides actionable insights for aspiring and established screen printing entrepreneurs.
1. Mastering the Basics
The foundation of a successful screen printing business lies in mastering the essential techniques and processes. This includes:
-
Understanding Equipment: Familiarize yourself with the various types of screen printing equipment available, such as manual and automatic presses, exposure units, and curing devices. Regular maintenance and proper setup are critical for achieving consistent quality.
-
Ink Selection: Choose the right inks for your projects. Whether using plastisol, water-based, or specialty inks, understanding their properties will enable you to produce high-quality prints that meet customer expectations.
-
Screen Preparation: Invest time in mastering screen preparation, from coating screens with emulsion to exposing and reclaiming them. Properly prepared screens are essential for achieving crisp, clear designs.
2. Emphasizing Quality Control
Quality control should be a top priority at every stage of the printing process. Implementing systematic quality checks will help you maintain high standards and ensure customer satisfaction:
-
Conduct Regular Tests: Perform test prints to check for color accuracy, registration, and print quality before starting full production runs.
-
Standardize Processes: Create standardized procedures for printing, curing, and finishing to minimize errors and ensure consistency across different jobs.
-
Seek Customer Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from customers to identify areas for improvement and adapt to their needs.
3. Fostering Creativity and Customization
The ability to offer unique and customized solutions can set your business apart from competitors. Embrace creativity by exploring advanced techniques and customization options:
-
Explore Design Tools: Utilize design software to create compelling graphics and streamline the design process. Offering personalized designs can attract a wider customer base.
-
Experiment with Specialty Inks: Incorporate specialty inks and techniques, such as metallic, glow-in-the-dark, or discharge printing, to enhance the appeal of your products.
-
Stay Informed on Trends: Keep up with industry trends and customer preferences to ensure your offerings remain relevant and attractive.
4. Effective Marketing Strategies
A strong marketing strategy is essential for attracting and retaining customers. Focus on both online and offline marketing tactics to build brand awareness:
-
Build an Online Presence: Create a professional website showcasing your portfolio, services, and customer testimonials. Leverage social media platforms to engage with your audience and promote your work.
-
Networking: Attend trade shows, local events, and industry conferences to connect with potential clients and industry peers. Building relationships can lead to valuable partnerships and referrals.
-
Leverage SEO and Content Marketing: Optimize your website for search engines and create informative content that addresses customer pain points, positioning yourself as an industry expert.
5. Managing Operations Efficiently
Efficient operations are crucial for scaling your screen printing business. Focus on streamlining processes to maximize productivity:
-
Invest in Technology: Utilize modern software solutions for inventory management, order tracking, and customer relationship management (CRM) to enhance operational efficiency.
-
Set Realistic Goals: Establish clear business goals and track your progress regularly. Use performance metrics to evaluate your success and make informed decisions for growth.
-
Focus on Customer Service: Provide exceptional customer service to build loyalty and encourage repeat business. Respond promptly to inquiries and address any issues that arise during the printing process.
6. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, incorporating sustainable practices can enhance your brand reputation:
-
Use Eco-Friendly Inks: Consider switching to water-based or eco-friendly inks and materials to appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
-
Implement Recycling Programs: Establish recycling initiatives for waste materials and encourage sustainable practices within your operations.
-
Promote Your Efforts: Highlight your commitment to sustainability in your marketing materials to attract customers who prioritize eco-friendly businesses.
Final Thoughts
Building a successful screen printing business is a journey that requires dedication, creativity, and adaptability. By mastering the fundamentals, emphasizing quality, fostering creativity, implementing effective marketing strategies, managing operations efficiently, and adopting sustainable practices, you can position your business for long-term success.
As you continue to grow your screen printing venture, remain open to learning, experimenting, and evolving with the industry. Embrace challenges as opportunities for improvement, and always keep your customers' needs at the forefront of your efforts. With perseverance and a commitment to excellence, you can establish a thriving screen printing business that stands out in a competitive marketplace.
If you have any further questions or need additional insights on specific areas, feel free to reach out!
Pre:Elevate Your Screen Printing Business with Top-Quality Screen Print Supplies
Next:Exploring Silk Screening Material: A Sales and Marketing Perspective
Tags: